This is summary of establishement company in China. Managing Partner Sigita Truksane went through this process establishing comany in Ningbo. Some steps and action can differ depending on business location place in China.
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) entered the implementation of the brand-new Foreign Investment Law (FIL) on January 1, 2020. The Sino-Foreign Equity Joint Venture Law, the Sino-Foreign Cooperative Joint Venture Law, and the Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) Law were the three foreign direct investment laws that were previously in place to regulate foreign invested entities (FIEs).
Establishing Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises or Joint Ventures in China
The structure that was picked, the classification of the entity, and the location can all affect how a FIE is set up. Service companies, manufacturing companies, and foreign-invested commercial enterprises (FICE) are the most common types.
After obtaining a business license, a trading company, for instance, must register with China Customs, while a manufacturing company must complete an environmental impact evaluation report. The set-up process will also be influenced by other options, such as financing an operation in China with a foreign loan or using equipment to fulfill registered capital obligations.
What are the steps to establish business in China?
STEP 1: BUSINESS STRATEGY
- What long- and short-term plans does the company have for its activities?
- Who will be in charge of the organization’s major roles?
- What financial commitments are required to operate the entity?
- How will you finance this investment?
- What is the projected cash flow for the upcoming 12 months?
- All of this information is necessary for the setup process and will also help you choose the best location and building for your business.
STEP 2: CONCLUDE RENT AGREEMENT
A) BUSINESS LOCATION – lease agreement and business location must be confirmed. Before your company can be officially established in China, you must have a confirmed business address.
Tip Sheet: If the incorporation application is rejected, it is suggested that a clause in the contract state that the lease can be canceled.
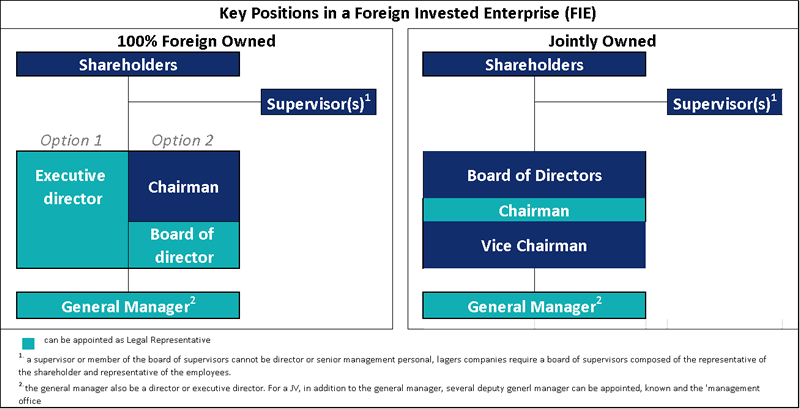
B) KEY PERSONS IN THE FIE – choose who will hold the most important positions in the FIE. The following positions will need to be filled if the company is to become a “Wholly Foreign Owned Enterprise” (WFOE) with 100 percent foreign ownership:
- Supervisor General manager
- Legal Representative
The options for a WFOE and a joint venture (JV) are depicted in the following diagram.
C) BUSINESS SCOPE
The scope of the business must be disclosed during the licensing phase of the registration process for FIEs. Your company’s China business classification will be determined by this, which is referred to as the “Business Scope.” The most prevalent classifications for FIEs currently operating in China are as follows:
- Service Provider: a FIE that provides services to businesses or consumers. The company may not typically manufacture or trade goods. Consulting, training, restaurants, and management services are all examples of services.
- Firm in Manufacturing: a FIE that makes products for sale. Manufacturing businesses may import raw materials for production and do not require an intermediary to sell goods locally or internationally. Manufacturing plants frequently necessitate additional certifications, so the registration procedure may be more complicated than for other types of businesses.
- FICE stands for Foreign-Invested Commercial Enterprise. In terms of business operations, FICE offers more adaptability. Retail, wholesale, and franchising are examples of these activities. A FICE typically receives both import and export rights upon establishment, though additional certifications from various bureaus are required to begin international trade. In China, FICEs can also buy and sell products without a middleman. Manufacturing FIEs can apply to include FICE capabilities in their business scope, and vice versa.
D) REGISTERED CAPITAL AND TOTAL INVESTMENT
The location and the type of business will have an impact on the minimum capital requirement for the majority of businesses. The officials who are assessing your application will decide if the investment you plan to make is enough to support your business activities. Companies established in Tier 1 Cities – CNY1 million (about 160,000 Eur) is as a baseline and operate under the assumption that the capital investment should be enough to pay two years’ worth of expenses. In the end, the investor should put up enough money to cover operating costs up until the point at which it is predicted that the FIE would generate a positive cash flow.
STEP 3: ONLINE APPLICATION
In Shanghai and most other well-developed cities, the company set-up process is streamlined through the online Administration for Industry & Commerce (AIC) portal. However some steps may be slightly different depending on location.
A) NAME APPROVAL
The first step in the online application is to choose a Chinese name for the entity.
Tip Sheet: Is your brand already known in China? Have ‘netizens’ already given you a Chinese name? If so, and it is available to use, then using that name will save you time and money.
Additional guidelines restrict the content of names, forbidding the use of content that either misleads consumers or hinders fair competition, or damages or contradicts national unity, policies, social ethics, culture or religion. Special characters, such as Arabic numerals, foreign symbols or alphabets, are not permitted, and certain words such as ‘China’, ‘Chinese’, ‘National’, ‘State’ or ‘International’ can only be used under limited circumstances.
B) BUSINESS LICENCE APPLICATION
When the name has been chosen, the next step is to fill in all the details regarding the business licence. This information should include (but is not limited to):
- Registered capital, total investment and investment period
- Registered address
- FIE classification
- Business scope
- Information on the key positions
STEP 4 APPLICATION IN HARD COPY
Hard copies of all the documentation must be gathered and given to the AIC during this phase. The crucial government process officially commences at this point. The following paperwork is required:
- lease document re-signed with the Chinese name of the company
- Passports for the general manager, supervisor, and executive directors
applications with signatures - Investor corporation documents
letter of commitment from each investor or their representative
appointment of the application representatives by power of attorney - Additional docs upon request
- The internet system must be used to upload these papers.
- The file should be finished within three working days after the commerce authorities, typically at the provincial level, have verified the integrity and completeness of the data.
Tip Sheet: Use a rollerball pen with black ink to sign your application; otherwise it will fail.
STEP 5: BUSINESS LICENSE
Registration and an application for a business license can be submitted to the local AIC within 30 days of receiving an Approval Certificate.
Tip Sheet: You now officially have a legal entity, but until it has a bank account or is registered with the local tax bureau, it won’t be very useful.
STEP 5: CARVING CHOPS
Every Chinese business must have an official “chop,” which is a round piece with the official company name in Chinese. If you’d rather have a chop with the English company name, you’ll need to submit another application. A company’s seal can be obtained from the local Public Security Bureau (PSB) following successful registration with the AIC.
A company must have a “legal representative chop,” a “financial chop,” a “fapiao chop,” and, in the case of a trading FIE, a “customs chop” in addition to the official company chop.
STEP 6: OPEN RMB BANK ACCOUNT AND FOREIGN EXCHANGE ACCOUNT
An FIE in China must have at least two bank accounts: a capital account in a foreign currency and a basic account in RMB. A FIE’s daily business operations in China require an RMB basic account. The company can only withdraw RMB cash from this account, which frequently serves as a designated account for tax payments. To receive foreign capital, you need to have a foreign currency capital account. You will need approval from the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE) in order to open such an account.
Tip Sheet: Choose one of the Chinese banks to open your capital and basic accounts with. It will be more simple. Don’t use a foreign bank to open them.
STEP 7 – GENERAL VAT TAXPAYER RELATED PROCEDURES
Once a business licence has been issued, the final step is to register with your local tax bureau. An FIE must register with the relevant tax bureau within 30 days. Generally, the application process takes ten working days. Companies are not required to hire an authorised agent for this process and can apply themselves. However, if the investor has used a registration service provider for the registration of the FIE, a tax application service will often be included.
The steps required to set up a FIE have been simplified over the years. However, components such as the amount and division of registered capital, or newly implemented regulations require in-depth knowledge. It is therefore vital to keep on top of any changes in order for the establishment process to run smoothly, particularly as a bad decision now will affect your operation in the future.